Oct 20, 2011
eHealth Strategies for Africa
At its simplest, an ehealth strategy begins as a direct component of a country’s health and health strategy. Ehealth is one of the resources needed for health. It is competing with other resources, such as more doctors, new drugs and new hospitals, so it should show how it offers benefits to the health of countries’ citizens and the performance of its healthcare system.Jun 23, 2010
EHEALTH SOLUTIONS IN THE AFRICAN REGION: CURRENT CONTEXT AND PERSPECTIVES
The World Health Organization (WHO) defines eHealth as the cost-effective and secure use of information and communication technologies (ICTs) for health and health-related fields.1 ICT provides a range of technologies for gathering, storing, retrieving, processing, analysing, transmitting and receiving data and information. These include radio, television, mobile phones, computer and network hardware and software, as well as the services and applications associated with them, including videoconferencing and distance learning. eHealth is an umbrella term that covers a variety of areas such as health informatics, digital health, telehealth, telemedicine, eLearning and mobile health.2Mar 1, 2010
An Assessment of e-Health Projects and Initiatives in Africa
The World Health Organization (WHO) has been spearheading the development of health in member countries. In 2005 member countries signed the WHA 58 Resolution which encourages member countries to implement e-Health as a tool of fostering healthcare service delivery for their populations. The WHO has therefore been partnering with the African Union, as well as other developmental bodies, to realize the goal of implementing e-Health in African countriesAug 7, 2015
Modeling antecedents of electronic medical record system implementation success in low-resource setting hospitals
With the increasing implementation of Electronic Medical Record Systems (EMR) in developing countries, there is a growing need to identify antecedents of EMR success to measure and predict the level of adoption before costly implementation. However, less evidence is available about EMR success in the context of low-resource setting implementations. Therefore, this study aims to fill this gap by examining the constructs and relationships of the widely used DeLone and MacLean (D&M) information system success model to determine whether it can be applied to measure EMR success in those settings.Mar 1, 2005
Critical Success Factors Relating to Healthcare’s Adoption of New Technology: A Guide to Increasing the Likelihood of Successful Implementation
Over the last decade, significant attention has been paid in both academic and professional literature to the healthcare information technology conundrum, which can easily be summarized in the following question: Why have we not seen more successful implementation of information technology in healthcare? While many theories and suggestions have been proposed, there can be no argument that none have been truly effective in explaining or helping to resolve this widespread problem. As a result, the healthcare field is becoming experienced in building not-so-effective systems.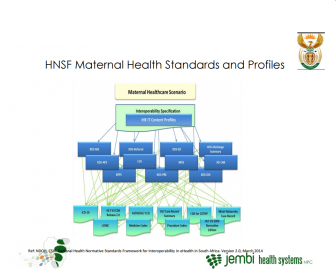
Aug 5, 2015
Webinar: Introduction to OpenHIE and Interoperability for National Information Systems
The Better Immunization Data Learning Network (BLN) recently held a webinar entitled “Introduction to OpenHIE and Interoperability for National Information Systems”. The presentation gave an introduction to the OpenHIE community, the concept of interoperability between solutions and showed how these patterns have been used in a national scale information system in South Africa, including linking systems to exchange data to DHIS.
Jan 1, 2006
Building FOUNDATIONS for eHealth
Every day, across the world, people make improvements in health as a direct benefit of information and communication technologies (ICT). eHealth innovations like electronic health records, computerassisted prescription systems and clinical databases are transforming health today, and hold even greater promise for the future. ICT support clinical care, provide health information to the general public and scientifi c information to professionals. They provide a platform for publishing, disseminating health alerts and supporting administrative functions.Oct 4, 2011
Broadband for Africa: Deploying broadband on an Unprecedented Scale
The African Internet has the highest data packet loss and the worst throughput figures of any region in the world. Moreover, the continent is about 18 years behind Europe in terms of performance and the situation is improving more slowly than other parts of the world, meaning the continent’s connectivity could be as much as 70 times worse than the developed world in a decade.Mar 1, 2010
An Assessment of e-Health Projects and Initiatives in Africa
The World Health Organization (WHO) has been spearheading the development of health in member countries. In 2005 member countries signed the WHA 58 Resolution which encourages member countries to implement e-Health as a tool of fostering healthcare service delivery for their populations. The WHO has therefore been partnering with the African Union, as well as other developmental bodies, to realize the goal of implementing e-Health in African countries .There has been a number of continental initiatives aimed at harnessing e-Health programmes in Africa. These initiatives include the Telemedicine Task Force, the Pan African e-Network and many other initiatives with developmental partners who are keen to fund e-Health programmes in Africa. The major challenges have been ensuring that these programmes will be sustainable and making sure that they can be harmonized. Most African countries do not have e-Health policies, e-Health strategies and so most require guidelines for implementation. Also almost all African countries have no e-Health budget in their fiscus. However there are over three hundred e-Health pilot projects underway or planned in Africa and most of them are neither scalable nor sustainable. The majority of projects examined for this report are funded by external donor agencies or were started as research projects. They mostly (and especially the latter) cease when the donor funding is exhausted. In contrast there are very few projects funded by the Ministries of Health from inception by African Countries.Jan 1, 2007
Journal of Health Informatics in Developing Countries – A review on barriers to implementing health informatics in developing countries
eHealth, eHealth Plan, Policies, Practices
Global
Health information systems are spreading globally which promote health and human prosperity. Globalization of health informatics infrastructures is needed to have significant growth in improving quality and capacity of healthcare sector in developing countries. At present the health information infrastructure remains inadequate to meet the needs of rising population. Poverty and technological implementations are major barriers in the lesser-developed countries. Health care can be transformed and health status of population improved by eliminating barriers and implementing health informatics in developing countries.
Jump in. Expand your knowledge.
Events
No upcoming events.
